Problem Statement
We have to implement the reverseList function that takes the head node of a linked list as an input
and returns the head node of the reversed linked list in the output.

Brute Force Solution
If we iterate over the input linked list and insert its value at the beginning of a new list the result would be a reversed linked list.

Psuedo-code for the Brute Force Solution
reversedLinkedList = LinkedList()
temp = linked_list.head
while(temp!=nil){
reversedLinkedList.insertAtStart(temp.value)
temp = temp.next
}
return reversedLinkedList
Time Complexity Analysis
Best Case Scenario
In the best-case scenario, the time complexity of the brute force solution will be $O(n)$ as it requires a loop over the input linked list.
Worst Case Scenario
The time complexity worst-case scenario for the brute force solution is the same as the best-case scenario i.e. $O(n)$.
Space Complexity Analysis
The brute-force solution assumes that we have enough memory space to store the input linked list and the reversed linked list in the memory at the same time. Thus, the space complexity of the brute force solution will scale linearly ($O(2n)$) to the size of the input data.
Code for Brute Force Solution
package main
import "fmt"
type ListNode struct {
Val int
Next *ListNode
}
func Display(ln *ListNode){
temp := ln
for(temp!=nil){
fmt.Printf("%d->", temp.Val)
temp=temp.Next
}
fmt.Println()
}
func insertAtStart(ln *ListNode, value int)(*ListNode){
tempNode := &(ListNode{Val:value, Next:ln})
return tempNode
}
func reverseList(ln *ListNode)(*ListNode){
// Creating a new linked list to store nodes in
// the reverse order
var reversedList *ListNode
temp := ln
for(temp!=nil){
// Inserting values at the start of the reversed
// linked list
reversedList = insertAtStart(reversedList, temp.Val)
temp=temp.Next
}
return reversedList
}
func main(){
ln := &(ListNode{Val:5})
ln.Next = &(ListNode{Val:2})
ln.Next.Next = &(ListNode{Val:3})
ln.Next.Next.Next = &(ListNode{Val:7})
ln.Next.Next.Next.Next = &(ListNode{Val:4})
fmt.Println("Input Linked List:")
Display(ln)
fmt.Println("Reversed Linked List:")
Display(reverseList(ln))
}
// Output
// Input Linked List:
// 5->2->3->7->4->
// Reversed Linked List:
// 4->7->3->2->5->
Optimized Solution
Since reversing a linked list will require traversal of all the nodes, the time complexity of the solution
could not be improved from $O(n)$. But if we could reverse the next node reference in place for each
node the space complexity would be reduced to $O(n)$.
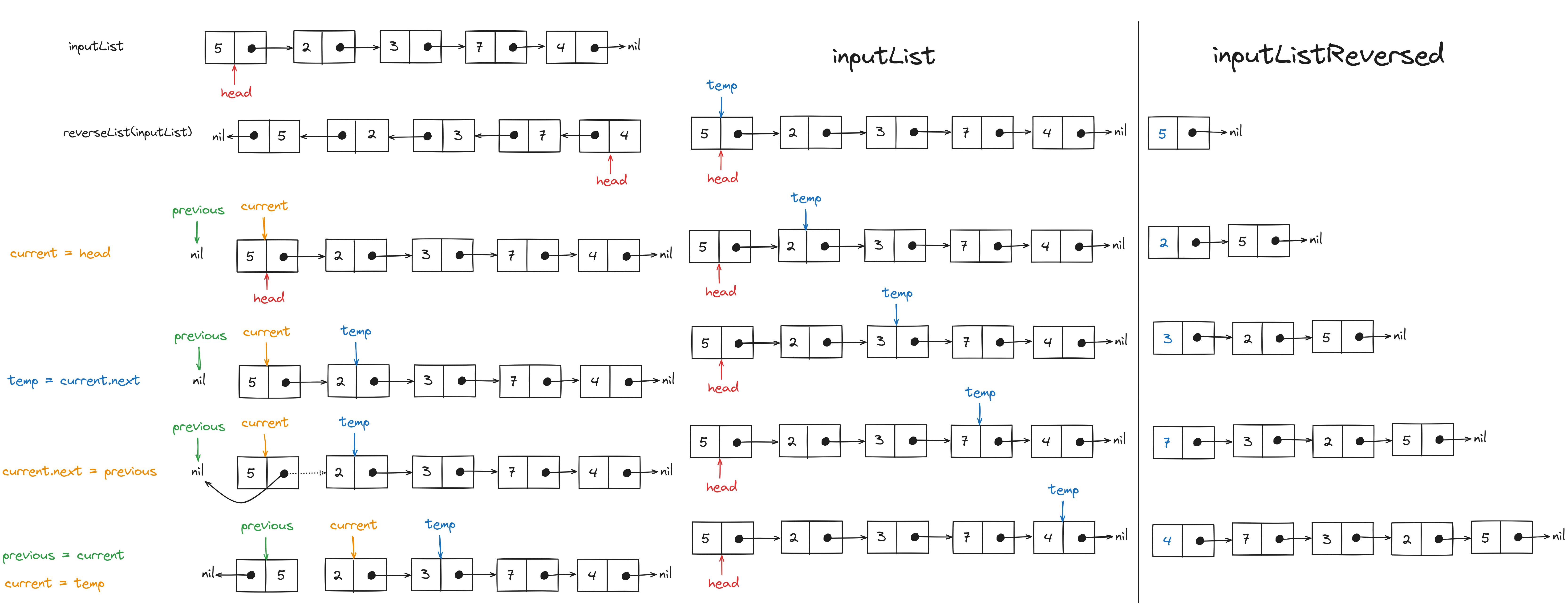
We will use the two-pointer approach to maintain references to nodes current and previous. The
current pointer will start from the head node and iterate till the nil at the end. Whereas, the
previous pointer will be one step behind the current.

At the end of the iteration, the previous pointer will be pointing to the head of the reversed linked list.
Psuedo code for the Optimized Solution
previous = none
current = head
while(current!=none){
temp = current.next
current.next = previous
previous = current
current = temp
}
return previous
Time Complexity Analysis
Best Case Scenario
We are iterating over the complete linked list so the time complexity is the same as the brute force solution i.e. $O(n)$.
Worst Case Scenario
The time complexity of the optimized solution for the worst-case scenario will also be $O(n)$.
Space Complexity Analysis
Unlike brute-force solution we are performing operations on the input linked list directly so we don’t need additional memory space and the space complexity will be $O(1)$.
Code for Optimized Solution
package main
import "fmt"
type ListNode struct {
Val int
Next *ListNode
}
func Display(ln *ListNode){
temp := ln
for(temp!=nil){
fmt.Printf("%d->", temp.Val)
temp=temp.Next
}
fmt.Println()
}
func reverseList(ln *ListNode)(*ListNode){
var prev *ListNode
curr := ln
for(curr!=nil){
// Storing the location of the node
// next to the current pointer
temp := curr.Next
// Changing next for the current node to
// the node pointed by the previous pointer
curr.Next = prev
// Moving the previous pointer one node forward
prev = curr
// Resetting current to the next node
// in iteration
curr = temp
}
return prev
}
func main(){
ln := &(ListNode{Val:5})
ln.Next = &(ListNode{Val:2})
ln.Next.Next = &(ListNode{Val:3})
ln.Next.Next.Next = &(ListNode{Val:7})
ln.Next.Next.Next.Next = &(ListNode{Val:4})
fmt.Println("Input Linked List:")
Display(ln)
fmt.Println("Reversed Linked List:")
Display(reverseList(ln))
}
Thank you for taking the time to read this blog post! If you found this content valuable and would like to stay updated with my latest posts consider subscribing to my RSS Feed.
Resources
206. Reverse Linked List
Reverse Linked List - Iterative AND Recursive - Leetcode 206 - Python